BEST: Two new biological reserves in La Reunion
With a unique flora and fauna, Reunion Island is one of the "hot spots" of global biodiversity, home to more than a thousand endemic species.
In order to preserve Réunion's exceptional yet threatened natural heritage, the French National Forestry Office (ONF) and the General Council of La Reunion, owner of Reunion's public forests, presented the BEST project: "Creation of new protected areas in public forests in Reunion Island and in Mayotte" in 2012.
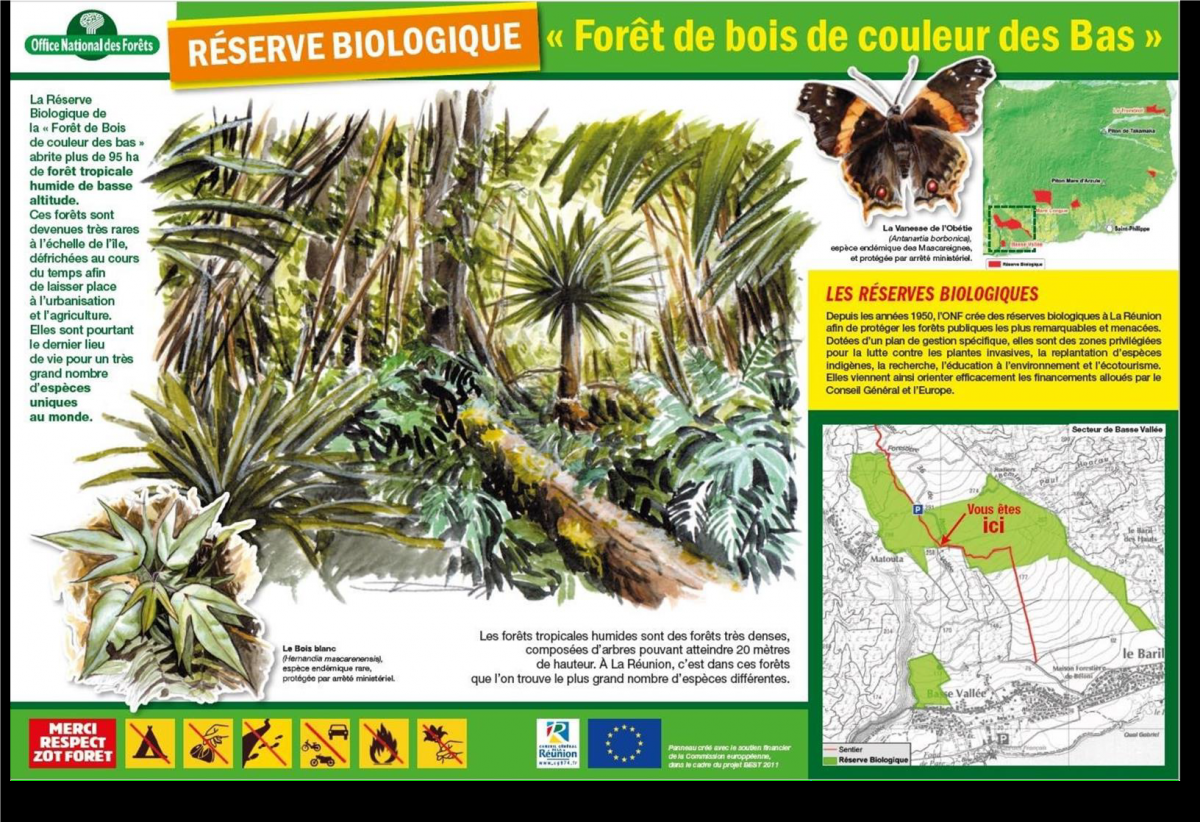
This mission was accomplished in June 2020 with the formal creation of two new reserves: the Directed Biological Reserves (RBD) of the Bois de couleur des bas forest and of the Saint-Philippe coast. Covering an area of nearly 300 hectares, these reserves ensure the protection of two low-altitude natural habitats that are very rare in the Mascarene Islands, and in the tropical zone: low-altitude humid forest and coastal vegetation. Located at the foot of the Piton de la Fournaise Volcano, both BRDs complete a network of protected areas representing 43% of the island territory.
Managed by the ONF, these reserves allow the implementation of a conservation management plan identifying issues and targets for conservation, as well as action plans against invasive species, poaching, or for the reproduction of rare and endangered species.
Upstream of the official creation of these new areas, the BEST project made possible to finance the preparatory work by supporting field conservation actions, the development of management plans, and a global strategy of protected areas for the completion of the national park. At the regional level, the project also contributed to develop the exchange of experience and best practices between La Reunion and Mayotte on the sustainable management of public forests and the conservation of biodiversity.
The island, whose "Pitons, cirques and ramparts" are part of the UNESCO World Heritage List, has also applied for the Green List.
* The latest assessments carried out as part of the red lists of threatened species for vascular flora and fauna reveal that 49 plant species have disappeared from the island and that 275 others are now threatened while birds and terrestrial reptiles are suffering a high rate of extinction - see red list of threatened species in France: https://uicn.fr/liste-rouge-france/