The COVID-19 pandemic drove the global tourism industry to a grinding halt. With would-be travelers stuck at home, many tourist destinations were left deserted. In the Global North, news articles and social media posts led us to believe that wildlife had flourished during our absence. The phrase ‘nature is healing’ became a popular refrain, following reports of decreased pollution and unanticipated animal sightings in urban areas.
But was nature really healing? In reality, the decline in global travel decimated essential income for many protected areas, where biodiversity and local communities need it most. The sudden drop in tourism led to job losses and food insecurity, forcing households to return to wildlife and natural resources to survive. Poaching surged in some places in the Global South.
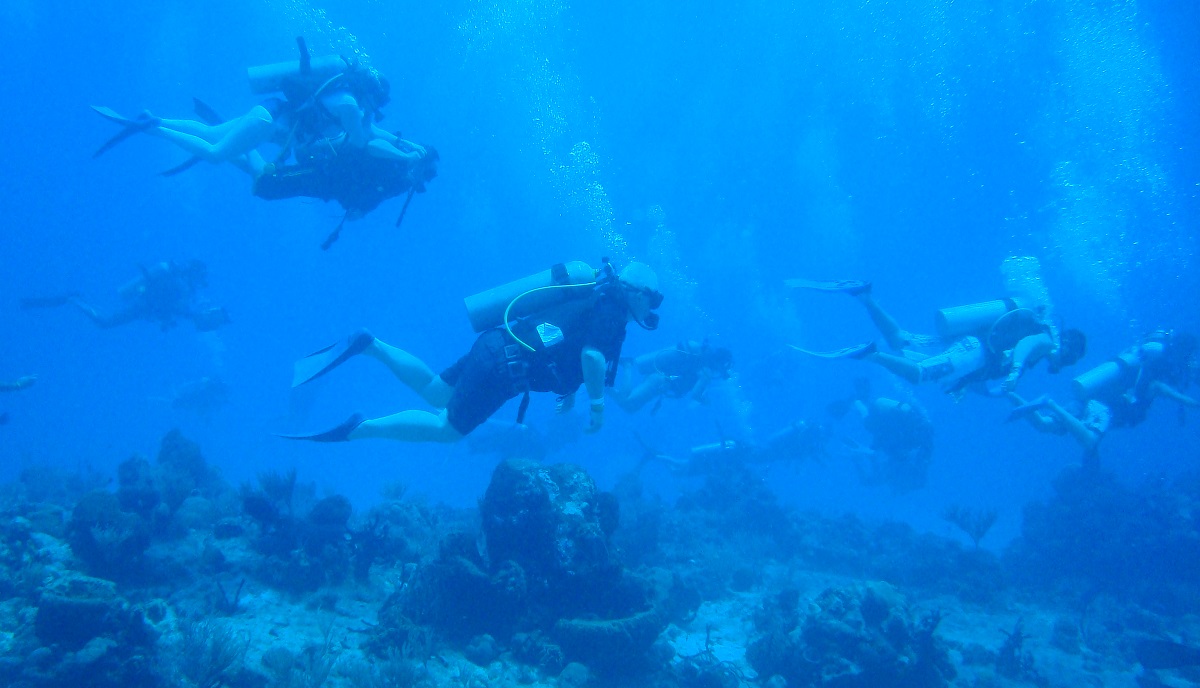
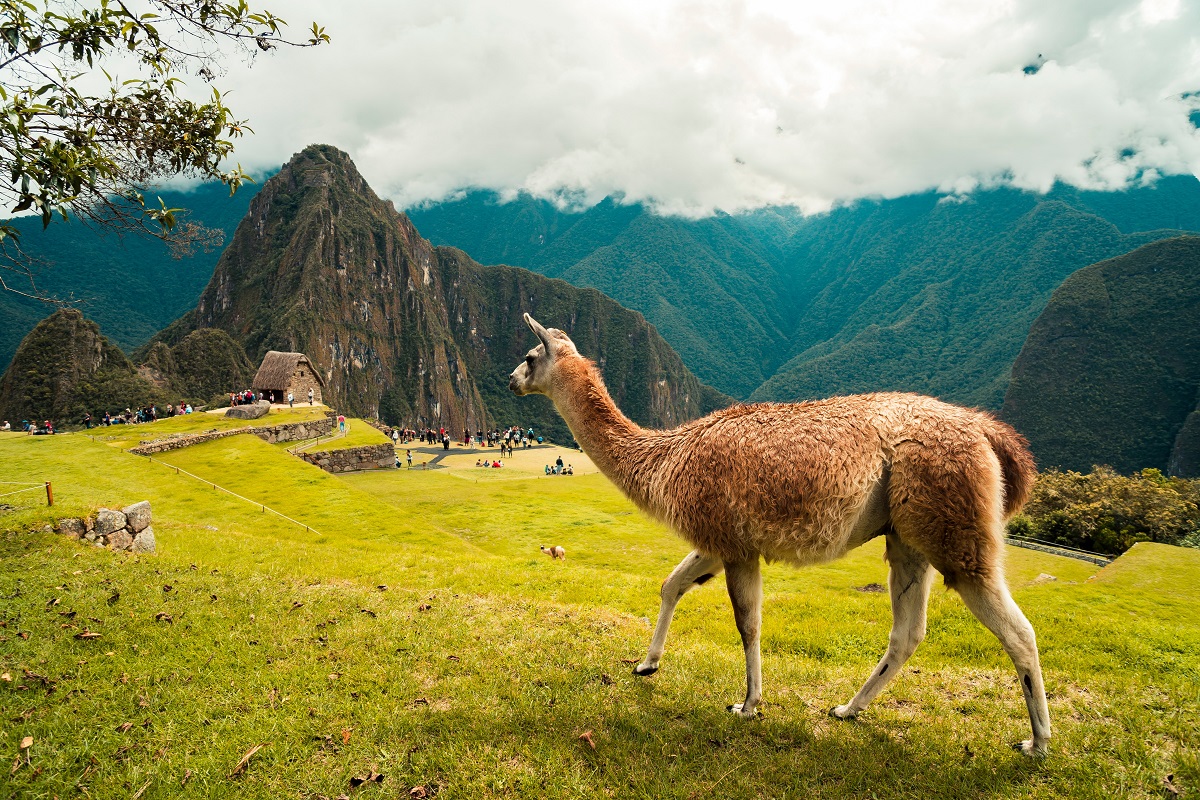
Before the pandemic, wildlife tourism had been steadily increasing. A 2019 study found that it had grown to have a direct economic value of USD 120 billion annually, providing over USD 344 billion of wider economic benefits and supporting 21.8 million jobs worldwide. With more visitors came more funding; with greater funding, better protection. For example, in the Philippines, Kenya and Zambia, over half of funding for protected areas comes from visitors. In Botswana, it’s more than 80%.
Mismanaged wildlife tourism can do more harm than good. Long before the pandemic, construction of infrastructure for tourists was a major cause of habitat loss.
However, research also shows that mismanaged wildlife tourism can do more harm than good. Long before the pandemic, the construction of large and luxurious accommodation, roads and other infrastructure for tourists was a major cause of habitat fragmentation and loss in popular destinations. Single-use disposables worsened plastic pollution problems. Greenhouse gas emissions from travel intensified climate change, and demand for extravagant food, hot showers and uninterrupted battery charging over-exploited local energy resources in remote areas.





Thank you
Thank you for outlining these important steps to make tourism nature-positive. These are reminders we all need to hear.
Monitoring the resolution
Very interesting, and good to see Resolution 130. That said, I don't quite get it. Can someone explain what the resolution calls for? For example, who and how will this resolution be monitored by the IUCN and others?
🌏 https://www.planeta.com/iucn2020-motion130
totally agree! Just happen…
totally agree!
Just happen to be a very fine Line between carrying capacity, Tourism-based development and Market (Price for travelling) and democratization of Tourism. At the end, natural areas should be take care way more than a Urban monument of a City, but how to compete to that kind of cheaper that can also hold larger amount of people. Perhaps, then is when tourism should be redesigned and clients be able to pay higher prices. And, in that way find the correct income threshold.
Nature-Positive Tourism
Hi - a very nice article, although I'm a little surprised it didn't refer directly to the Nature-Positive report recently produced by the World Travel and Tourism Council and specifically the accompanying tool-box to enable companies of all sizes to develop nature-positive action plans? While I've heard some suggest the toolbox is too challenging for businesses to engage with, I'm not convinced this is case and think we need case studies and examples to showcase the successes and challenges...
Questions about the report
Interesting. Downloading the report now - https://action.wttc.org/vision-for-nature-positive-travel-and-tourism - and asking how this vision and toolbox will be used in a practical manner. I will be updating links on Planeta.
Add new comment