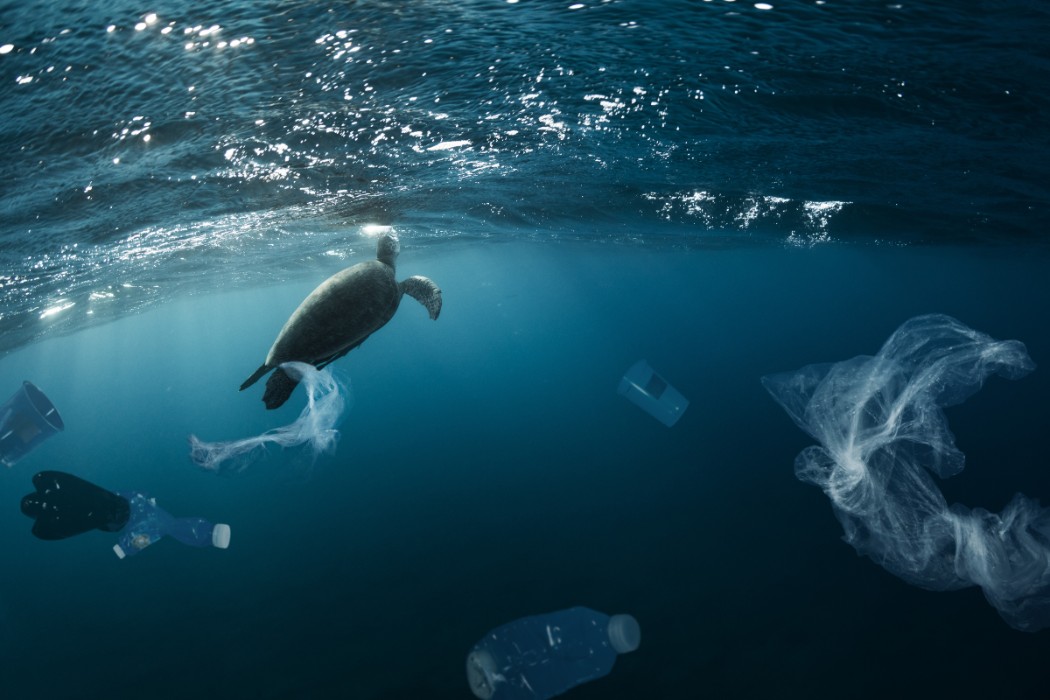
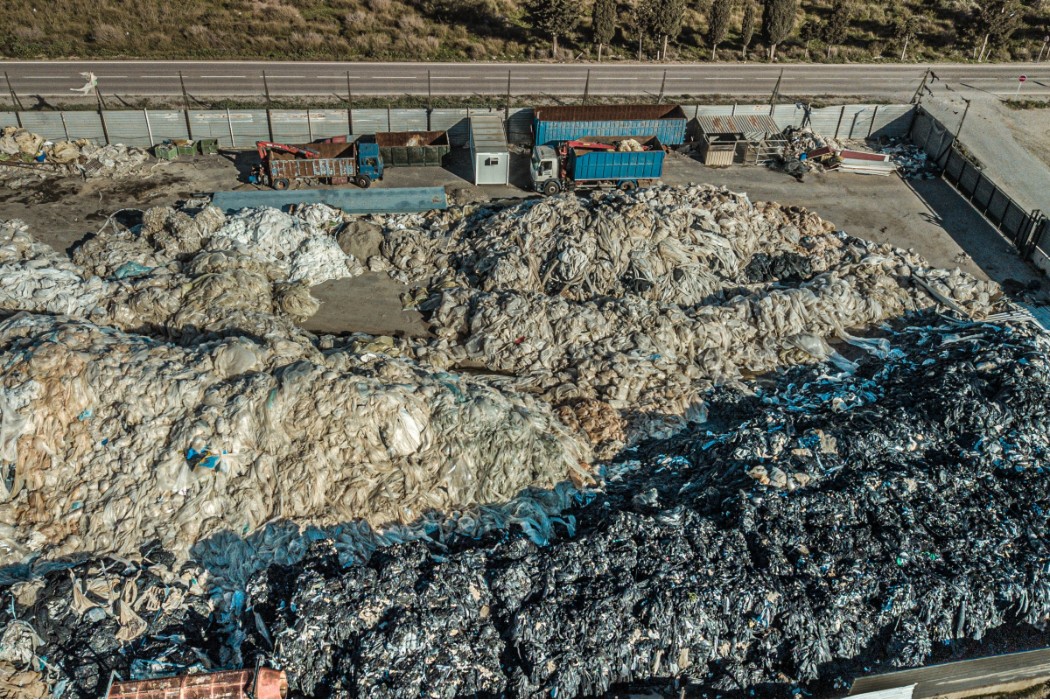
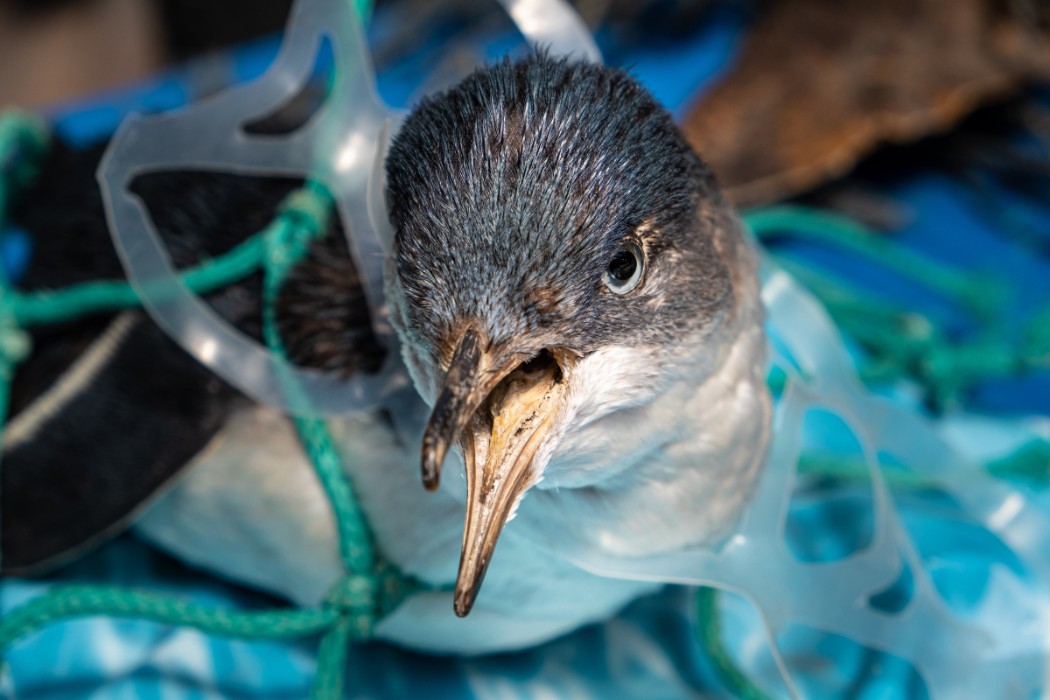
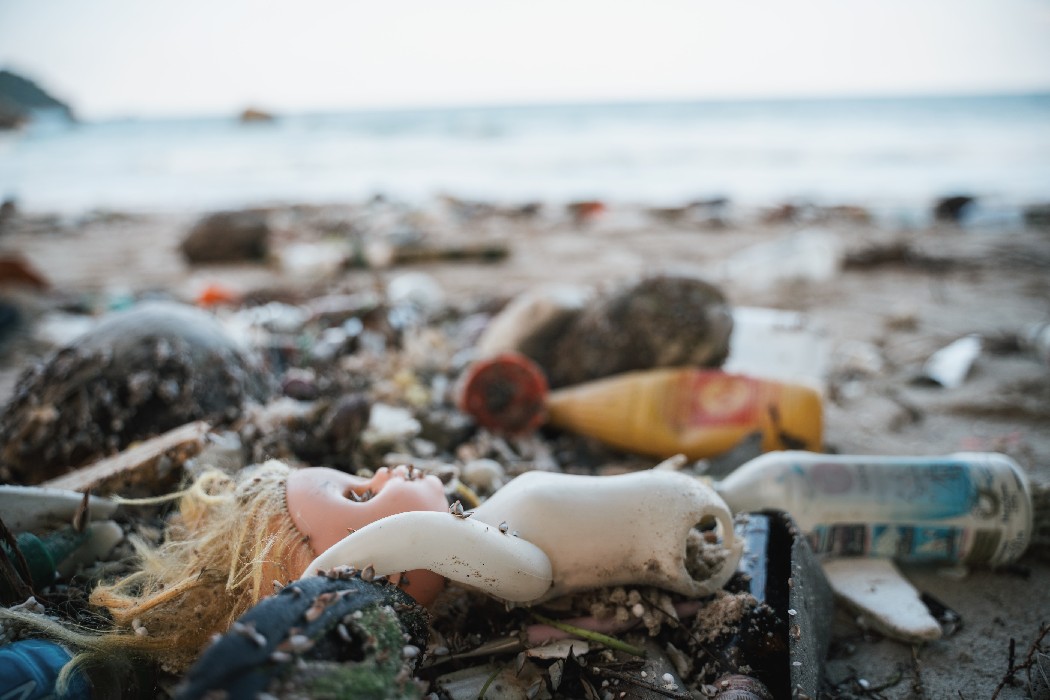
Where does ocean plastic come from?
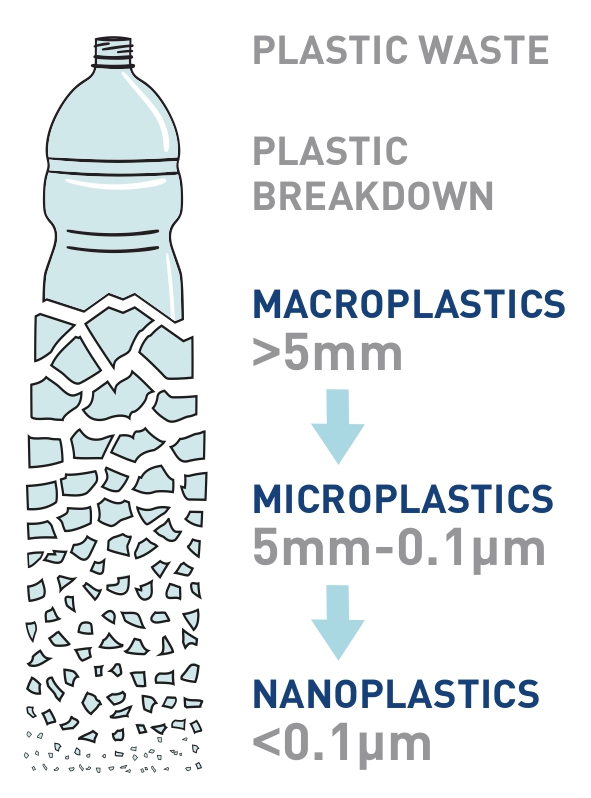
Overall, 80% of marine plastic debris comes from land, and 20% is produced by ocean-based sources such as fishing, shipping and aquaculture. 3 Much of it is comprised of industrial and domestic waste from metropolitan and urban areas with poorly managed collection and disposal systems. Rubbish finds its way into rivers and other waterways, sometimes through storm drains and sewage outfalls, and these take it all the way to the sea. It’s estimated that 94% of the plastic pollution that enters the Mediterranean comes in the form of macroplastics, but microplastic pollution is significant too. Land-based sources of microplastics include agricultural polyethylene sheets that fragment from weathering, biosolids and sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants, and grey water from washing clothes made with synthetic fibres. 4 Sewage entering municipal treatment systems is high in microfibres from textiles, microplastics from personal care products, and degraded consumer products.

















